Sign a request and verify the signature
To ensure the authenticity and integrity of data after transmission, Antom requires all requests to be signed and the signatures to be verified:
- When calling an API, you must sign the request sent to Antom and verify the Antom response signature accordingly.
- When receiving a notification, you must verify the signature of the received notification. However, you do not need to sign the response for the notification.
Using Antom libraries for request signing and signature verification can significantly streamline your programming tasks and expedite the process of adding and validating API signatures. For more details about using Antom libraries for signing and signature verification, see Use Antom libraries.
If you prefer not to use Antom libraries, you can sign a request and verify the signature by customized coding, see Customized coding.
Use Antom libraries
This section guides you on using Antom libraries to sign a request and verify the signature when calling an API and receiving a notification from Antom. All available Antom libraries can be found in SDKs.
Call an API
Before calling an API, ensure that you have generated a pair of asymmetric public and private keys on the Antom Dashboard. For more information, see Generate keys.
Send Request & Handle Response
If you make an API call using Antom libraries, the signing and verification process will be done automatically. Taking Java as an example, follow these steps to use Antom libraries:
- Add Maven dependency
- Send a request and verify the signature
1. Add maven dependency:
You can find the latest version on GitHub.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alipay.global.sdk</groupId>
<artifactId>global-open-sdk-java</artifactId>
<version>{latest_version}</version>
</dependency>2. Send a request and verify the signature
The following code sample shows how to use Java to send a request and verify the signature:
import java.util.UUID;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.alipay.global.api.AlipayClient;
import com.alipay.global.api.DefaultAlipayClient;
import com.alipay.global.api.exception.AlipayApiException;
import com.alipay.global.api.model.ams.*;
import com.alipay.global.api.model.constants.EndPointConstants;
import com.alipay.global.api.request.ams.pay.AlipayPayRequest;
import com.alipay.global.api.response.ams.pay.AlipayPayResponse;
@RestController
public class PaymentByAntomLibrary {
/**
* replace with your client id
* find your client id here: <a href="https://dashboard.alipay.com/global-payments/developers/quickStart">quickStart</a>
*/
public static final String CLIENT_ID = "";
/**
* replace with your antom public key (used to verify signature)
* find your antom public key here: <a href="https://dashboard.alipay.com/global-payments/developers/quickStart">quickStart</a>
*/
public static final String ANTOM_PUBLIC_KEY = "";
/**
* replace with your private key (used to sign)
* please ensure the secure storage of your private key to prevent leakage
*/
public static final String MERCHANT_PRIVATE_KEY = "";
private final static AlipayClient CLIENT = new DefaultAlipayClient(
EndPointConstants.SG, MERCHANT_PRIVATE_KEY, ANTOM_PUBLIC_KEY, CLIENT_ID);
@RequestMapping("/pay")
public Object pay() {
AlipayPayRequest alipayPayRequest = composePayRequest();
AlipayPayResponse alipayPayResponse = null;
try {
// automatically sign and verify
alipayPayResponse = CLIENT.execute(alipayPayRequest);
} catch (AlipayApiException e) {
String errorMsg = e.getMessage();
// handle error condition
}
return alipayPayResponse;
}
private AlipayPayRequest composePayRequest() {
AlipayPayRequest alipayPayRequest = new AlipayPayRequest();
alipayPayRequest.setProductCode(ProductCodeType.CASHIER_PAYMENT);
// replace with your paymentRequestId
String paymentRequestId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
alipayPayRequest.setPaymentRequestId(paymentRequestId);
// set amount
Amount amount = Amount.builder().currency("SGD").value("4200").build();
alipayPayRequest.setPaymentAmount(amount);
// set paymentMethod
PaymentMethod paymentMethod = PaymentMethod.builder().paymentMethodType("PAYNOW").build();
alipayPayRequest.setPaymentMethod(paymentMethod);
// replace with your orderId
String orderId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
// set buyer info
Buyer buyer = Buyer.builder().referenceBuyerId("yourBuyerId").build();
// set order info
Order order = Order.builder().referenceOrderId(orderId)
.orderDescription("antom testing order").orderAmount(amount).buyer(buyer).build();
alipayPayRequest.setOrder(order);
// set env info
Env env = Env.builder().terminalType(TerminalType.WEB).build();
alipayPayRequest.setEnv(env);
// replace with your notify url
alipayPayRequest.setPaymentNotifyUrl("https://www.yourNotifyUrl.com");
// replace with your redirect url
alipayPayRequest.setPaymentRedirectUrl("https://www.yourMerchantWeb.com");
return alipayPayRequest;
}
}Receive a notification
After receiving a notification from Antom, verify the signature of the request. The process of verifying the request signature is similar to the process introduced in the Send Request & Handle Response section. Follow these steps to verify the signature:
- Obtain the Antom public key for the request to verify the signature.
- Get the
request-time、client-id、signaturefrom the request header. - Verify the signature.
The following code sample shows how to use Java to verify the signature:
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.alipay.global.api.model.Result;
import com.alipay.global.api.model.ResultStatusType;
import com.alipay.global.api.response.AlipayResponse;
import com.alipay.global.api.tools.WebhookTool;
@RestController
public class PaymentNotifyHandleByAntomLibrary {
/**
* replace with your antom public key (used to verify signature)
* find your antom public key here: <a href="https://dashboard.alipay.com/global-payments/developers/quickStart">quickStart</a>
*/
private static final String SERVER_PUBLIC_KEY = "MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEAtERCOmPp2N/lIqamK/FqSzHOaPhzWamQhacIfnj+auDp10xhGESQDUsrUFnWBC6LVdJVhfsJVeyHKr6ciaAATEHhicCoNAzZw5Vp8lrIUXXtArqAHZJu7ow7rVNXJ64WD/gYQANCtlnvOMIlv5bA7pX6ORepjtc4TTZStskA/ffRShconhILjYUxdzadU6FCER88i7eVJpDAHdhtN5Nwwlh/zfJGGyEbav1DpwatexxkwqB6Qj0nYJ2Iv+8OOhZMZqdFv5AHyj4u+c4T4d+8y7lySkmCIIIzhwMM7ykglAwXiHOenLA23OGjG5nqxtzRQ9cfdhdJx9Ih2XvG3yOJdQIDAQAB";
/**
* payment result notify processor
* using <a href="https://spring.io">Spring Framework</a>
*
* @param request HttpServletRequest
* @param notifyBody notify body
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/pay/notify/antom")
public Object payNotifyHandler(HttpServletRequest request, @RequestBody String notifyBody) {
// retrieve the required parameters from http request.
String requestUri = request.getRequestURI();
String requestMethod = request.getMethod();
// retrieve the required parameters from request header.
String requestTime = request.getHeader("request-time");
String clientId = request.getHeader("client-id");
String signature = request.getHeader("signature");
Result result;
AlipayResponse response = new AlipayResponse();
try {
// verify the signature of notification
boolean verifyResult = WebhookTool.checkSignature(requestUri, requestMethod, clientId,
requestTime, signature, notifyBody, SERVER_PUBLIC_KEY);
if (!verifyResult) {
throw new RuntimeException("Invalid notify signature");
}
// deserialize the notification body
// update the record status with notify result
// respond the server that the notification is received
result = new Result("SUCCESS", ResultStatusType.S, "success");
} catch (Exception e) {
String errorMsg = e.getMessage();
// handle error condition
result = new Result("ERROR", ResultStatusType.F, errorMsg);
}
response.setResult(result);
return ResponseEntity.ok().body(response);
}
}Customized coding
Before you begin, gain a basic understanding of the Antom message structure.
Call an API
Before calling an API, ensure that you have generated a pair of asymmetric public and private keys on the Antom Dashboard. For more information, see Generate keys.
Sign a request
The following figure shows how to sign a request:
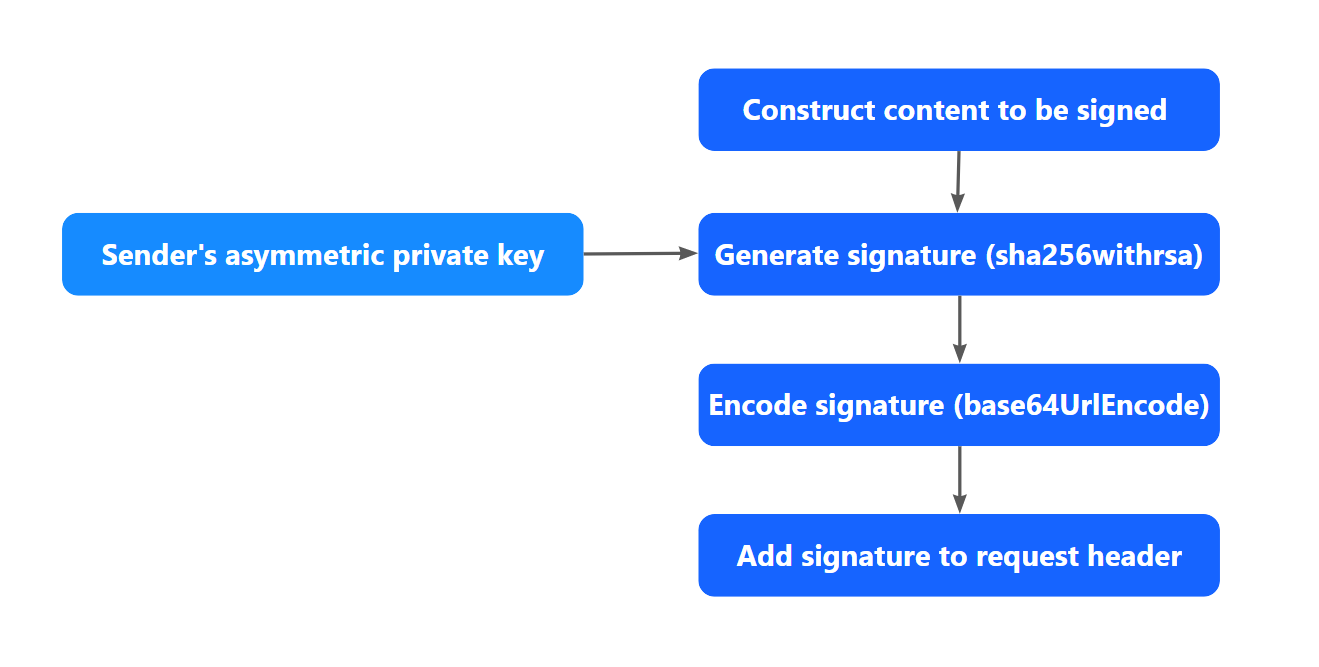
Figure 1. How to sign a request
Step 1: Construct the content to be signed
The syntax of content_to_be_signed is as follows:
<http-method> <http-uri>
<client-id>.<request-time>.<request-body>Note: A space character is needed between <http-method> and <http-uri>.
http-method: HTTP Request Method. The value is alwaysPOST.http-uri: including Path to Resource and Parameters (If have). For example, if the HTTP URL is https://open-na-global.alipay.com/ams/api/v1/payments/pay, this field is/ams/api/v1/payments/pay.client-id: this param is required in Request Header and is used to identify a client. An example value isSANDBOX_5X00000000000000.request-time: this param is required in Request Header and it specifies the timestamp of when a request is sent. The value of this field must be accurate to milliseconds. An example value is1685599933871.request-body: HTTP Request Body. See the example code below:
{
"env": {
"terminalType": "WEB"
},
"order": {
"orderAmount": {
"currency": "CNY",
"value": "100"
},
"orderDescription": "Testing order",
"referenceOrderId": "ORDER_ID_1685599933871"
},
"paymentAmount": {
"currency": "CNY",
"value": "100"
},
"paymentMethod": {
"paymentMethodType": "ALIPAY_CN"
},
"paymentRedirectUrl": "https://www.example.com",
"paymentRequestId": "REQUEST_ID_1685599933871",
"productCode": "CASHIER_PAYMENT"
}By complying with the syntax of content_to_be_signed, the request body above is constructed as follows:
POST /ams/api/v1/payments/pay
SANDBOX_5X00000000000000.1685599933871.{
"env": {
"terminalType": "WEB"
},
"order": {
"orderAmount": {
"currency": "CNY",
"value": "100"
},
"orderDescription": "Testing order",
"referenceOrderId": "ORDER_ID_1685599933871"
},
"paymentAmount": {
"currency": "CNY",
"value": "100"
},
"paymentMethod": {
"paymentMethodType": "ALIPAY_CN"
},
"paymentRedirectUrl": "https://www.example.com",
"paymentRequestId": "REQUEST_ID_1685599933871",
"productCode": "CASHIER_PAYMENT"
}Step 2: Generate the signature
The syntax of generating the signature is as follows:
generated_signature=urlEncode(base64Encode(sha256withRSA(<content_to_be_signed>, <privateKey>)))generated_signature: the generated signature string.urlEncode: the method to encode the base64 encoded digital signature.base64Encode: the method to encode the generated digital signature.sha256withrsa: the method to generate a digital signature for the provided content.content_to_be_signed: the content obtained from Step 1.privateKey: the private key value.
An example of a generated signature is as follows:
SVCvBbh5Eviwaj13ouTDy%2FAqFcNDNLXtoIgxFurTgnYjfBJ6h7jl4GKr%2Bkw8easQv9EHK7CXT9QZOMrkYNOUuqRs%2FDtT4vROCiRcnqNOKVjU3zHt%2Br%2Fxal%2FYRV4dc%2FNtu1ppyWJ6a2xNFCa63Y2YKNn%2FW%2B9eABmU2oohVXwBNoCnaLDoTIJV2RKb3E%2FiUp0aIWUz0Ntv4kVR8ZqMe6DUmf7pHRq9hm2av4wwBpJbHC%2B6R%2BMBQPv%2F0ZUFBW02ie%2FTpXBrPasb15s%2FjcmRpAnmED%2FFIec4TGzDIHr%2BO3QFtIRu72vg4zHWC3FuL4i8zfMXWNi3kp7hBFUIBpYroTZH5Q%3D%3DThe following code sample shows how to use Java to sign a request:
import java.net.URLEncoder;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.security.KeyFactory;
import java.security.PrivateKey;
import java.security.spec.PKCS8EncodedKeySpec;
import java.util.Base64;
public class SignatureSampleCode {
/**
* your private key, used to sign
* please ensure the secure storage of your private keys to prevent leakage
*/
private static final String CLIENT_PRIVATE_KEY = "";
/**
* you clientId
*/
private static final String CLIENT_ID = "";
/**
* @param requestURI domain part excluded, sample: /ams/api/v1/payments/pay
* @param clientId your clientId, sample: SANDBOX_5X00000000000000
* @param requestTime timestamp in milliseconds, sample: 1685599933871
* @param privateKey your private key
* @param requestBody request body
* @return
*/
public static String sign(String requestURI, String clientId, String requestTime, String privateKey, String requestBody) {
// content_to_be_signed
String contentToBeSigned = String.format("POST %s\n%s.%s.%s", requestURI, clientId, requestTime, requestBody);
try {
// sha256withRSA
java.security.Signature signature = java.security.Signature.getInstance("SHA256withRSA");
// privateKey
PrivateKey priKey = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA").generatePrivate(
new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(Base64.getDecoder().decode(privateKey.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8))));
signature.initSign(priKey);
signature.update(contentToBeSigned.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
// sign
byte[] signed = signature.sign();
// base64Encode
String base64EncodedSignature = new String(Base64.getEncoder().encode(signed), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
// urlEncode
return URLEncoder.encode(base64EncodedSignature, StandardCharsets.UTF_8.displayName());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(sign("/ams/api/v1/payments/pay", CLIENT_ID, "1685599933871", CLIENT_PRIVATE_KEY, "{\n" +
" \"env\": {\n" +
" \"terminalType\": \"WEB\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"order\": {\n" +
" \"orderAmount\": {\n" +
" \"currency\": \"CNY\",\n" +
" \"value\": \"100\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"orderDescription\": \"Testing order\",\n" +
" \"referenceOrderId\": \"ORDER_ID_1685599933871\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"paymentAmount\": {\n" +
" \"currency\": \"CNY\",\n" +
" \"value\": \"100\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"paymentMethod\": {\n" +
" \"paymentMethodType\": \"ALIPAY_CN\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"paymentRedirectUrl\": \"https://www.example.com\",\n" +
" \"paymentRequestId\": \"REQUEST_ID_1685599933871\",\n" +
" \"productCode\": \"CASHIER_PAYMENT\"\n" +
"}"));
}
}
Step 3: Add the generated signature to the request header
- Assemble a signature string based on the following syntax:
'Signature: algorithm=<algorithm>, keyVersion=<key-version>, signature=<generatedSignature>'algorithm: specifies the digital signature algorithm that is used to generate the signature. RSA256 is supported.keyVersion: specifies the key version that is used to generate or validate the signature. By default, the value is the latest version of the key associated with Client-Id.generatedSignature: the signature generated in Step 2.
For example:
'Signature: algorithm=RSA256, keyVersion=1, signature=SVCvBbh5Eviwaj13ouTDy%2FAqFcNDNLXtoIgxFurTgnYjfBJ6h7jl4GKr%2Bkw8easQv9EHK7CXT9QZOMrkYNOUuqRs%2FDtT4vROCiRcnqNOKVjU3zHt%2Br%2Fxal%2FYRV4dc%2FNtu1ppyWJ6a2xNFCa63Y2YKNn%2FW%2B9eABmU2oohVXwBNoCnaLDoTIJV2RKb3E%2FiUp0aIWUz0Ntv4kVR8ZqMe6DUmf7pHRq9hm2av4wwBpJbHC%2B6R%2BMBQPv%2F0ZUFBW02ie%2FTpXBrPasb15s%2FjcmRpAnmED%2FFIec4TGzDIHr%2BO3QFtIRu72vg4zHWC3FuL4i8zfMXWNi3kp7hBFUIBpYroTZH5Q%3D%3D'- Add the signature string to the request header. For details about the request header, see the Message structure chapter.
Send a request
Construct a request by adding the Client-Id, Request-Time, and Signature properties to the request header. After a request is constructed, you can use common tools, such as cURL or Postman to send the request. In the following example, cURL is used:
curl -X POST \
https://open-na-global.alipay.com/ams/api/v1/payments/pay \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'Client-Id: SANDBOX_5X00000000000000' \
-H 'Request-Time: 1685599933871' \
-H 'Signature: algorithm=RSA256, keyVersion=1, signature=SVCvBbh5Eviwaj13ouTDy%2FAqFcNDNLXtoIgxFurTgnYjfBJ6h7jl4GKr%2Bkw8easQv9EHK7CXT9QZOMrkYNOUuqRs%2FDtT4vROCiRcnqNOKVjU3zHt%2Br%2Fxal%2FYRV4dc%2FNtu1ppyWJ6a2xNFCa63Y2YKNn%2FW%2B9eABmU2oohVXwBNoCnaLDoTIJV2RKb3E%2FiUp0aIWUz0Ntv4kVR8ZqMe6DUmf7pHRq9hm2av4wwBpJbHC%2B6R%2BMBQPv%2F0ZUFBW02ie%2FTpXBrPasb15s%2FjcmRpAnmED%2FFIec4TGzDIHr%2BO3QFtIRu72vg4zHWC3FuL4i8zfMXWNi3kp7hBFUIBpYroTZH5Q%3D%3D' \
-d '{
"env": {
"terminalType": "WEB"
},
"order": {
"orderAmount": {
"currency": "CNY",
"value": "100"
},
"orderDescription": "Testing order",
"referenceOrderId": "ORDER_ID_1685599933871"
},
"paymentAmount": {
"currency": "CNY",
"value": "100"
},
"paymentMethod": {
"paymentMethodType": "ALIPAY_CN"
},
"paymentRedirectUrl": "https://www.example.com",
"paymentRequestId": "REQUEST_ID_1685599933871",
"productCode": "CASHIER_PAYMENT"
}'Handle a response
After receiving a response from Antom, verify the signature of the response. The following figure shows how to verify a signature:
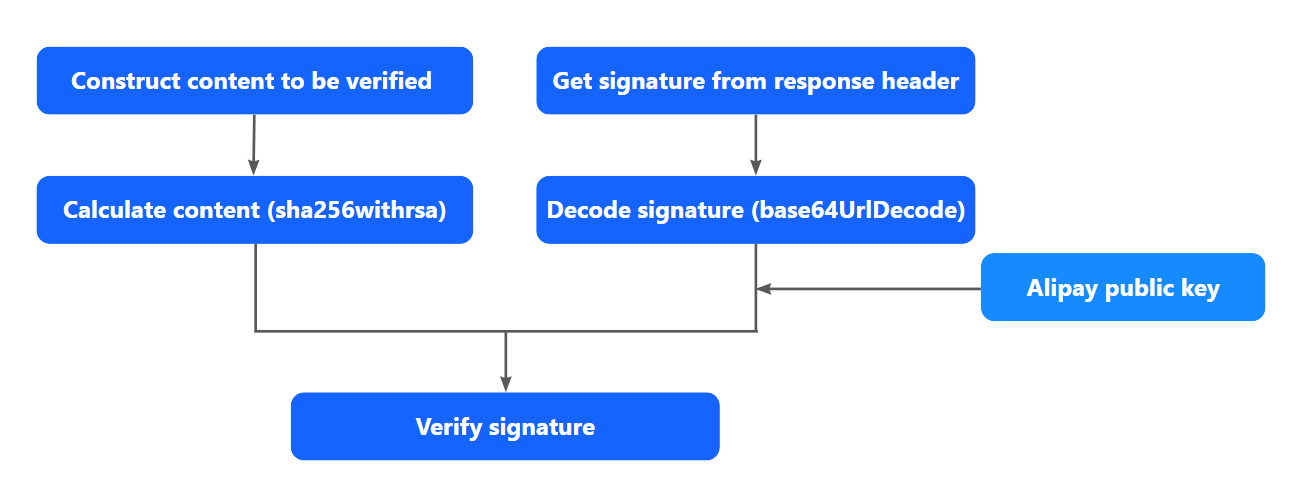
Figure 2. How to verify a signature
A response consists of the response header and the response body. The following codes show samples of the response header and body.
- Code sample of the response header:
Client-Id: SANDBOX_5X00000000000000
Response-Time: 2019-05-28T12:12:14+08:00
algorithm=RSA256,keyVersion=1,signature=d1jdwMNkno7eOFqbsmCl2lfnmAUlK40VyHi3%2FlIrto%2FdV%2F1Ds730bfNJc9YrqNzjfb3ly66bhF0vlxgaPPwYqsWmc3FSXqSQGdSZ42VOzoZXBA2sjI0e%2F8e7IIa%2FGlrzbpNwrOiMuJxaUw6lIK7vxxyvr8vxpfQ0Pml0mKnQO2NP4yY%2BvMMJCdvmM3Bl7mNYL%2BVCLDMNespD763EY252vqMU8fbC9CUf2zCckN78TaWOuK%2FOiMlVYN8VUYIKeoyutiNUv%2B0vIiqfq7IcXCS0pom33MltFukhiyHIso3B%2FD1KN9fi0B9eJbXPB5ox%2FLsChGS48rQECRiqo2mC%2FHXzyQ%3D%3D- Code sample of the response body:
{
"result": {
"resultCode": "SUCCESS",
"resultStatus": "S",
"resultMessage": "success"
}
}The following steps demonstrate how to handle a response from Antom by using the examples above.
Step 1: Obtain Antom public key
Obtain the Antom public key through Antom Dashboard > Developer > Quick start > Integration resources and tools > Integration resources.
Note: Only when you upload your asymmetric public key to Antom Dashboard, can you obtain the Antom public key used to verify the corresponding response from Antom.
Step 2: Construct the content to be verified
The syntax of content_to_be_validated is as follows:
<http-method> <http-uri>
<client-id>.<response-time>.<response-body>http-method: HTTP Request Method. The value is alwaysPOST.http-uri: including Path to Resource and Parameters (If have). For example, if the HTTP URL is https://open-na-global.alipay.com/ams/api/v1/payments/pay, this field is/ams/api/v1/payments/pay.client-id: this param is returned in Response Header and is used to identify a client. An example value isSANDBOX_5X00000000000000.response-time: this param is returned in Response Header and it specifies the time when a response is returned. The format of this param is as defined by ISO 8601. An example value is2019-05-28T12:12:14+08:00.response-body: HTTP Response Body.
By complying with the syntax of content_to_be_validated, construct the response given above as follows:
POST /ams/api/v1/payments/pay
SANDBOX_5X00000000000000.2019-05-28T12:12:14+08:00.{
"result": {
"resultCode":"SUCCESS",
"resultStatus":"S",
"resultMessage":"success"
}
}Step 3: Get the signature from the response header
The target signature string (target_signature) can be extracted from the Signature header in the response header. For details about the response header, see Message structure.
Code sample of Signature: Signature: algorithm=RSA256,keyVersion=1,signature=<target_signature>
Step 4: Verify the signature
The syntax of validating the signature is as follows:
is_signature_validate=sha256withRSA_verify(base64Decode(urlDecode(<target_signature>), <content_to_be_validated>, <serverPublicKey>))is_signature_validate: a Boolean value that specifies whether the signature is valid.
- true: the signature is valid.
- false: the signature is not valid. The cause can be a mismatch between the private key and public key, or
content_to_be_validatedis not correctly constructed.
sha256withRSA_verify: the method to verify the signature.base64Decode: the method to decode the digital signature.urlDecode: the method to decode the base64 decoded digital signature.target_signature: the target signature obtained from step 3.content_to_be_validated: the content to be verified, created from step 2.serverPublicKey: the Antom public key obtained from step 1.
The following sample code shows how to use Java to verify the signature:
import java.net.URLDecoder;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.security.KeyFactory;
import java.security.PublicKey;
import java.security.spec.X509EncodedKeySpec;
import java.util.Base64;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
public class SignatureSampleCode {
/**
* alipay public key, used to verify signature
*/
private static final String SERVER_PUBLIC_KEY = "";
/**
* you clientId
*/
private static final String CLIENT_ID = "";
/**
* @param requestURI domain part excluded, sample: /ams/api/v1/payments/pay
* @param clientId your clientId, sample: SANDBOX_5X00000000000000
* @param responseTime formated time as defined by ISO 8601, sample: 2019-05-28T12:12:14+08:00
* @param alipayPublicKey alipay public key
* @param responseBody response body
* @param targetSignature signature to be verified
* @return
*/
public static boolean verify(String requestURI, String clientId, String responseTime, String alipayPublicKey, String responseBody, String targetSignature) {
// targetSignature would not be present in the response when AMS returns a SIGNATURE_INVALID
if (StringUtils.isBlank(targetSignature)) {
return false;
}
// content_to_be_validated
String contentToBeValidated = String.format("POST %s\n%s.%s.%s", requestURI, clientId, responseTime, responseBody);
try {
// sha256withRSA
java.security.Signature signature = java.security.Signature.getInstance("SHA256withRSA");
// alipay public key
PublicKey pubKey = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA").generatePublic(
new X509EncodedKeySpec(Base64.getDecoder().decode(alipayPublicKey.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8))));
signature.initVerify(pubKey);
signature.update(contentToBeValidated.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
// urlDecode
String urlDecodedSignature = URLDecoder.decode(targetSignature, StandardCharsets.UTF_8.displayName());
// base64Decode
byte[] signatureToBeVerified = Base64.getDecoder().decode(urlDecodedSignature);
// verify
return signature.verify(signatureToBeVerified);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(verify("/ams/api/v1/payments/pay", CLIENT_ID, "2019-05-28T12:12:14+08:00", SERVER_PUBLIC_KEY, "{\"result\":{\"resultStatus\":\"S\",\"resultCode\":\"SUCCESS\",\"resultMessage\":\"success.\"}}", "d1jdwMNkno7eOFqbsmCl2lfnmAUlK40VyHi3%2FlIrto%2FdV%2F1Ds730bfNJc9YrqNzjfb3ly66bhF0vlxgaPPwYqsWmc3FSXqSQGdSZ42VOzoZXBA2sjI0e%2F8e7IIa%2FGlrzbpNwrOiMuJxaUw6lIK7vxxyvr8vxpfQ0Pml0mKnQO2NP4yY%2BvMMJCdvmM3Bl7mNYL%2BVCLDMNespD763EY252vqMU8fbC9CUf2zCckN78TaWOuK%2FOiMlVYN8VUYIKeoyutiNUv%2B0vIiqfq7IcXCS0pom33MltFukhiyHIso3B%2FD1KN9fi0B9eJbXPB5ox%2FLsChGS48rQECRiqo2mC%2FHXzyQ%3D%3D"));
}
}Receive a notification
After receiving a notification from Antom, verify the signature of the request. The process of verifying the request signature is similar to the process introduced in the Handle a response section. To verify the signature, follow these steps:
- Obtain the Antom public key for the request to verify the signature.
- Construct the request to be verified by complying with the syntax of
content_to_be_validated:
<http-method> <http-uri>
<client-id>.<request-time>.<notify-body>- Get the signature from the request header.
- Verify the signature.
